
Tests show bacteria that causes the severe form of pneumonia known as Legionnaires’ disease has resurfaced at a West Virginia-run hospital, health officials said.
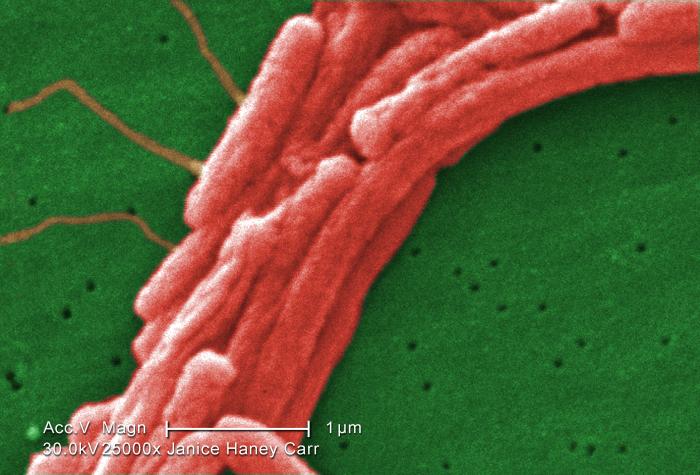
Source of bacteria that causes illness is still under investigation, Public Health says

New research led by the University of Birmingham suggests that skin cancer patients could have a better prognosis if their T cells send messages from five specific genes in their immune response to drugs given to treat the disease.
Over the past decade, scientists have been exploring vaccination as a way to help fight cancer. These experimental cancer vaccines are designed to stimulate the body's own immune system to destroy a tumor, by injecting fragments of cancer proteins found on the tumor.

Microbes that live in hot springs and hydrothermal vents have long fascinated scientists for their ability to survive at temperatures exceeding 100°C. Now, these “extremophiles” are piquing interest for another reason: They may hold a clue to longevity in much more complex creatures, including people.

Accumulation of amyloid beta (Aβ) in the brain in Alzheimer disease drives pathophysiology. A study in this issue of PLOS Biology revealed that Aβ from the liver can promote brain pathology, supporting that peripheral Aβ can contribute to neurodegeneration.

Despite increased clinical experience with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus -2 (SARS-CoV-2) and its resulting disease, coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19), and a rapidly expanding body of literature, the relationship between common risk factors and mortality from COVID-19 remains incompletely understood.

Mechanical ventilation systems are used in residences to introduce ventilation air and dilute indoor-generated pollutants.

A team of researchers at The Hong Kong Polytechnic University has developed what they describe as a fast and inexpensive way to test for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in human patients. The results are published in the journal Science Advances.

New research shows that Multiple Sclerosis (MS) patients undergoing anti-CD20 (aCD20) treatment—which depletes the B cells that contribute to the MS attacks—are able to mount robust T-cell responses to the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines, despite having a muted antibody response to the vaccines.







