
Gene therapy has partly restored the function of the retina's cone receptors in two children who were born completely color blind, reports a new study led by University College London (UCL) researchers.

Three newly published studies in Open Forum Infectious Diseases detail COVID-19 deaths in 2020 and 2021, including one describing an increase in US hospital deaths during a community surge, one finding a rise in the risk of dying at home in North Carolina, and one showing a reduced risk of hospital death in New York City in the second pandemic wave.

Use of human challenge models could enable a better understanding of the interactions between S. pneumoniae exposure, colonisation and subsequent mucosal and systemic immunity in humans with obesity.

By estimating people's brain age from MRI scans using machine learning, a team led by UCL researchers has identified multiple risk factors for a prematurely aging brain.

When babies in the African countries of Guinea Bissau and Uganda were given the tuberculosis vaccine, something remarkable happened. Instead of the vaccine only protecting against the target bacteria – Myocbacterium tuberculosis – the tuberculosis vaccine offered broad protection against a range of unrelated infections, including respiratory infections and serious complications such as sepsis.
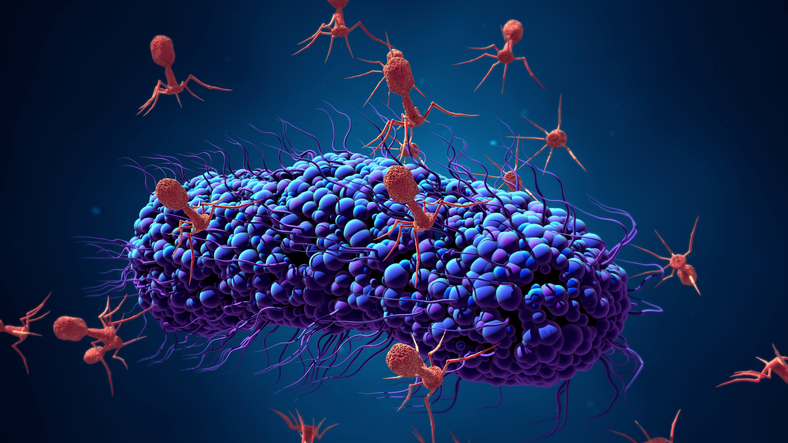
Decades after being slighted in favor of antibiotics, phages are attracting interest as therapeutic candidates that can overcome bacterial resistance

Major depressive disorders are characterized by a significant health burden, including changes in appetite and body weight. Identifying biomarkers such as changes in brain function to treat depression is difficult due to the varying symptomatology of affected individuals.

The immune system has evolved to safeguard the body from a wildly diverse range of potential threats. Among these are bacterial diseases, including plague, cholera, diphtheria and Lyme disease, and viral contagions such as influenza, Ebola virus and SARS CoV-2.

Inflammation is the body's first line of defense, occurring as droves of immune cells rush to the site of injury or acute illness to make repairs and stem further damage.

About 10% of the population in high income regions like Europe and the United States has been diagnosed with one or multiple autoimmune disorders. Examples are rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, systemic sclerosis, lupus erythematosus and type I diabetes. Although earlier research has suggested associations between some of these disorders and a higher risk of cardiovascular disease, these studies were often too small and limited to selected autoimmune or selected cardiovascular conditions to draw conclusive evidence on the necessity of cardiovascular disease prevention among patients with autoimmune disease, until now.







